While we try to answer some of the below questions that the investors ask:
“Which mutual fund schemes should one buy this year?”
“Which is the best mutual fund scheme?”
“Which is the best investment?”
“Should I invest in stocks or real estate?”
“What is your view of the stock market?”
“Are my investments proper? Or should I make some changes?”
We often overlook the investor needs while trying to answer such questions. Before trying to choose the right mutual funds, or any other instrument for your investment, you need to understand the investors’ needs first.
- Financial Goals: Investments are linked to financial goals like children’s education, retirement, or buying a house.
- For example, Shalini’s parents want to support her dream of becoming a space scientist, which requires financial planning for her education.
- Goal Setting: Prioritize goals based on importance and timeline (short-term vs. long-term).
- Rabindra, an engineer, is planning for his retirement, a long-term goal. Surinder Singh wants to buy a house in the near future, a short-term goal.
Seven Habits of Highly effective people (by Stephen R Covey)
| Urgent | Not Urgent | |
| Important | ||
| Not Important |
Important but not-so-urgent tasks are not planned for in time until they become urgent.
- Inflation: Account for inflation, which erodes purchasing power over time.
- For instance, if Shalini’s higher education costs Rs. 50 lakhs today, it will cost significantly more in 10 years due to inflation. (₹ 1,07,94,625 after 10 years)
- While a future expense will depend on a lot of factors like course/university selected, but it is important to keep a baseline expense adjusted for inflation
- Savings vs. Investments: Saving is setting aside money, while investing aims to grow it.
- Saving is considered akin to ensuring the safety of money,
- Investment is done primarily with the objective of earning profit.
- Investment Factors: Evaluate investments based on:
- Safety (risks involved),
- liquidity (ease of converting to cash),
- returns (income or capital gains),
- Convenience (ease of investment, ease to take out money, check value of investments),
- ticket size (minimum investment),
- Taxability (lower tax, more tax before maturity),
- Tax deductions (e.g. ELSS)
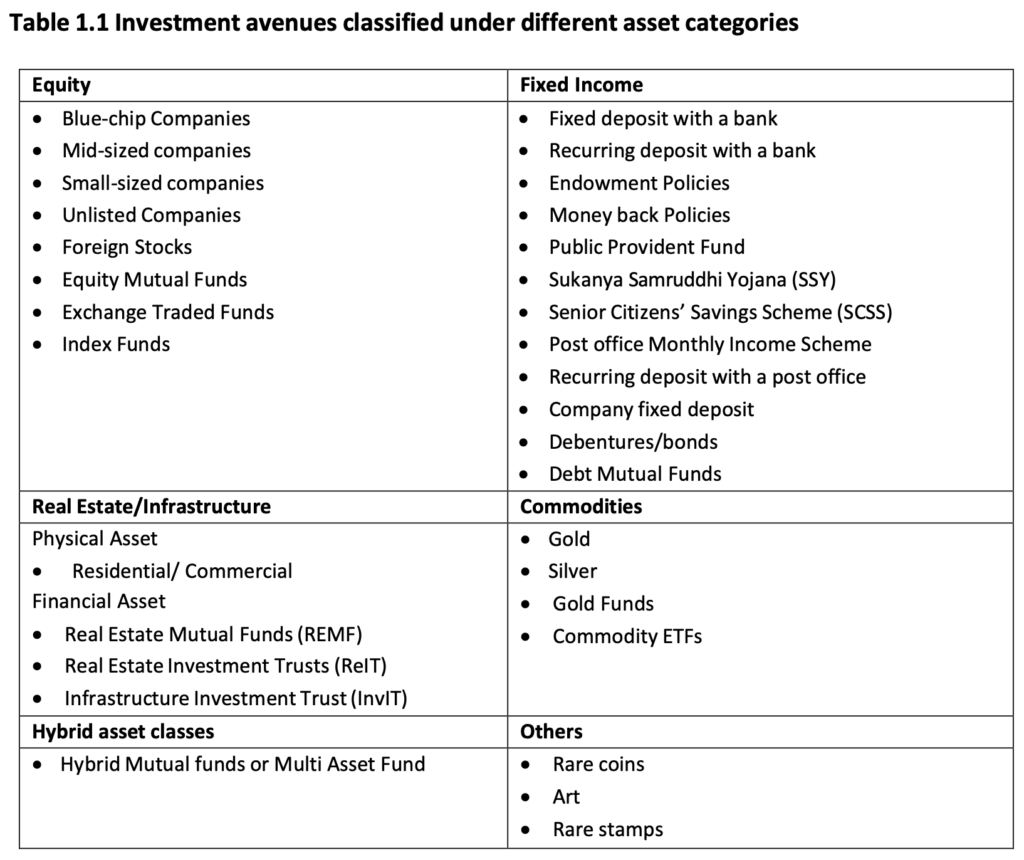
- Asset Classes: Major asset classes include real estate, commodities, fixed income, and equity.
- Real Estate:
- In majority of cases, individuals purchase real estate for self-occupation
- Can be for self-occupation or investment, but location is critical, and it’s relatively illiquid.
- Commodities:
- Commodity contracts – largely short term contracts, allows large exposure with small money
- Includes gold and silver, which can be used as investment avenues.
- Fixed Income:
- Includes bonds and debentures, which can provide regular income.
- If person holds bonds till maturity, in almost all cases, there would be no capital gains
- A transaction on bonds in secondary market – capital gains or losses
- Equity:
- Represents ownership in a business and carries risks and potential for higher returns.
- Equity share prices fluctuate a lot. However, over long periods of time, the share price follows the growth of the company. Historically, equity investing has generated returns in excess of inflation
- Equity share owners also receive dividends from the company
- Real Estate:
- Investment Risks: Mainly includes – Inflation risk, Liquidity risk, Credit risk, Market risk and Price risk
- Inflation Risk:
- For example, if inflation is 8% p.a., Rs. 10,000 today will be worth only Rs. 6,800 in purchasing power after 5 years.
- Liquidity Risk:
- Government securities offer safest investment, but to realise them without capital gains, need to hold them till maturity
- Low liquidity in real estate, pre-mature withdrawal penalty in FDs
- Credit Risk:
- Issue of bond does not pay or pay with delay
- Market Risk and Price Risk:
- Market Risk: When the price of all securities in a market falls due to a macro event like war, etc.
- Industry specific risk/First specific risk
- Interest Rate Risk:
- Interest rate Increases, Bond prices fall
- Drop in interest rate, increases value of investment
- Longer maturity Instruments = More fluctuations
- Inflation Risk:
| Risk Management | Diversification and asset allocation are key strategies for managing risk. – Avoid: Avoid certain instruments based on your risk profile. – Speculate: Take a position based on a certain expected event in the market, like falling interest rates. – Diversify: Diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk. |
| Behavioral Biases | Be aware of biases like overconfidence, herd mentality, and loss aversion, which can negatively impact investment decisions. For example, investors may miss out on critical information due to reliance on immediate examples or experiences. |
| Asset Allocation | Diversify investments across different asset classes to balance risk and return. Strategic asset allocation aligns with an individual’s financial goals, considering factors like return requirements, time horizon, and risk profile. |
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions.

Leave a Reply